Space & Time Complexity of JavaScript
Author: Doe Hoon LEE
When examining how performant an algorithm is, we can use (1) Time Complexity and (2) Space Complexity.
Time Complexity
the number of operations to run for an algorithm to complete its task
we can use Big O Notation to express time complexity and here are four complexity cases put in order (fastest to slowest) assuming sufficiently LARGE n
- Constant => O(1)
the size of input does not affect the number of operations or the amount of time it takes for an algorithm to complete
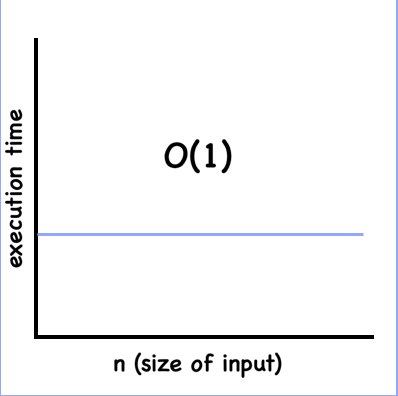
function bigOconstOne(n) {
return n * 2;
}
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
function bigOconstTwo(n) {
return arr[0] + arr[n.length-1];
}
- Logarithmic => O(log n)
the amount of time needed for an algorithm to complete its task gradually decreases
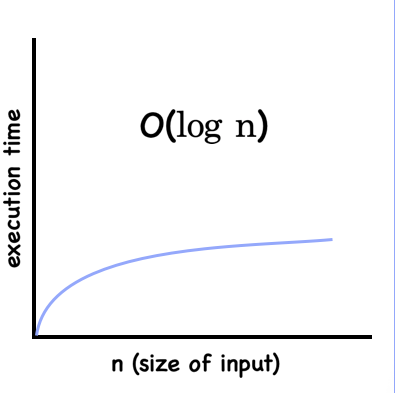
note. Binary Search is an example
- Linear => O(n)
execution is directly proportional to the size of input (graph is linear)
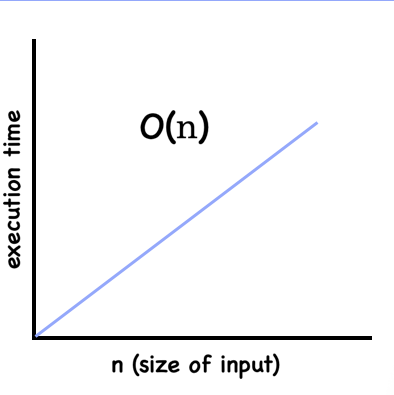
function linear(n) {
for (let i=0; i < n; i++) {
// do something
}
}
- Quadratic => O(n^2)
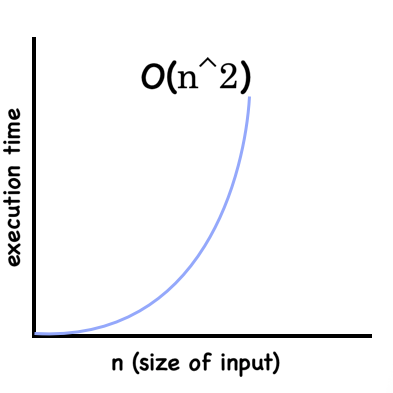
const arr = ["A", "B", "C", ... "x", "y", "z", ...];
function nestedLoop(arr) {
for (let i=0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j=0; j < arr.length; j++>) {
// do something
}
}
}
Space Complexity
amount of memory that the algorithm reuiqres to store its variables
| Data Type | Space Required |
|---|---|
| Number | O(1) space |
| Boolean | O(1) space |
| undefined | O(1) space |
| null | O(1) space |
| String | O(n) space |
| Array | O(n) space |
| Object | O(n) space |
Leave a comment