How To Read And Write Files With NodeJS
Author: Doe Hoon LEE
As usual, I am starting my post with JavaScript :)
Today, we are going to learn how to read files using Node.js
Do we need to install anything? Nope
BUT! we do need nodejs installed, obviously :p
Let’s begin!
Hmm.. well, to “READ” a file, we “NEED” a file though.. !!
echo 'Hello World!' > sample.txt

Why don’t we create a sample text file with "Hello World!" in it?!
Oh! Let’s not forget to create a JS file too!
touch fileReader.js
Inside the fileReader.js
import * as fs from 'fs';
const dataRead = fs.readFile('sample.txt', (err, data) => {
const dataRead = data.toString();
console.log(dataRead);
});
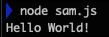
YAY!!
I personally use readFile and writeFile more for dealing with JSON.
So let’s try that!
BUT! Why don’t we create JSON with writeFile? So it will be the opposite xD
writeFile
import * as fs from 'fs';
const sampleDATA = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
gender: 'male',
location: 'Korea'
}
const data = JSON.stringif(sampleDATA);
fs.writeFile('sampleData.json', data, (err) => {
if (err) console.error(err);
console.log('Task Complete!');
})
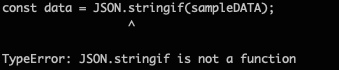
OOOPS!! What is going on?!
Well, I intentionally made a typo to see how we get an error message with
if (err) console.error(err);
It is always better when it tells us where or what went wrong :)
So, shall we correct the typo and redo it?
import * as fs from 'fs';
const sampleDATA = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
gender: 'male',
location: 'Korea'
}
const data = JSON.stringify(sampleDATA);
fs.writeFile('sampleData.json', data, (err) => {
if (err) console.error(err);
console.log('Task Complete!');
})
Then~~ we can try reading what we just wrote!
import * as fs from 'fs';
const dataRead = fs.readFile('sampleData.json', (err, data) => {
const dataRead = data.toString();
console.log(dataRead);
});

As usual, thanks for reading and participating in the activity :)
HAPPY CODING THEN!!
Leave a comment